10.4 代码实现
10.4.1 主页实现
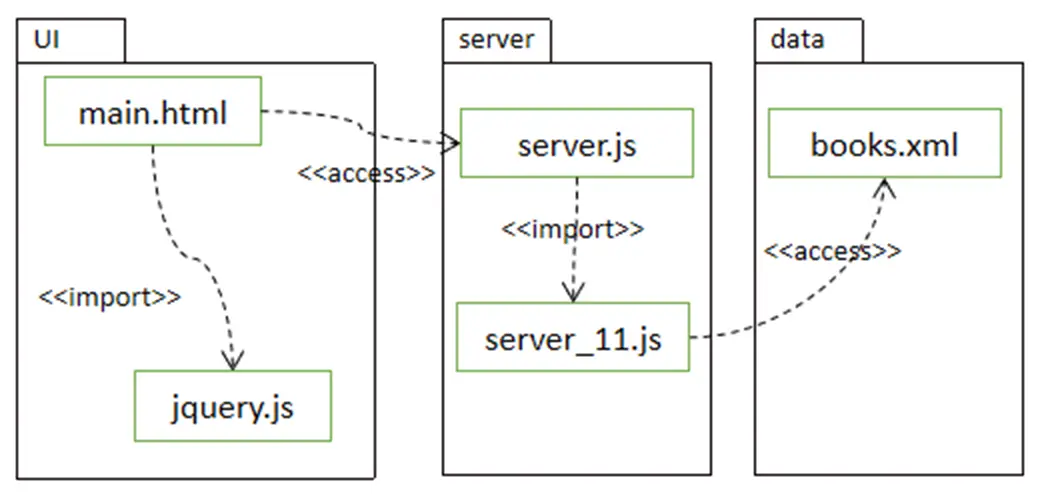
对应文件:main.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<title></title>
</head>
<body>
<h3>NodeJS读取XML测试</h3>
<hr />
<input type="button" value="查看原始XML文档" onclick="view_XML()" />
<input type="button" value="查看格式化XML文档" onclick="view_formatXML()" />
<hr />
<div id="result"></div>
</body>
</html>
<script type="text/javascript" src="jquery-1.11.1.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" >
//查看原始
function view_XML() {
var xhttp = new XMLHttpRequest();
xhttp.open("post","http://localhost:1007/readXML",true);
xhttp.onreadystatechange = function () {
if (xhttp.status == 200 && xhttp.readyState == 4) {
alert(xhttp.responseText);
}
}
xhttp.send();
}
//查看格式化XML文档
function view_formatXML() {
var xhttp = new XMLHttpRequest();
xhttp.open("post", "http://localhost:1007/readXMLToTable", true);
xhttp.onreadystatechange = function () {
if (xhttp.status == 200 && xhttp.readyState == 4) {
$("#result").html(xhttp.responseText);
}
}
xhttp.send();
}
</script>
10.4.2 后台主服务程序实现
对应文件:server.js
// JavaScript source code
//---------------请将这个文件保存为Unicode格式,否则麻烦大大的--------------
const http_obj = require("http");//用于产生服务对象
const fs_obj = require("fs");//读写后台文件
const url_tran_obj = require("url");//解释URL
const server = http_obj.createServer(function (request, response) {
//请求路径处理
var req_str = decodeURI(request.url);
var req_head;
var POS = req_str.indexOf("?");
if (POS == -1) { req_head = req_str; }
else { req_head = req_str.substring(0, POS); }
//设置查询对象
var url_obj = url_tran_obj.parse(req_str, true);
var Q_obj = url_obj.query;
//响应头设置
response.setHeader("Content-Type", "text/plain;charset=utf-8");
response.setHeader("Access-Control-Allow-Origin", "*");//实现跨域访问
response.writeHead(200);
//%%%%%%%%%%%%%-----------begin your code
require("./10/server/server_10.js")(request, response, req_head, Q_obj, fs_obj);
//%%%%%%%%%%%%%------------end your code
});
server.listen(1007);
console.log("Server is running at port 1007...");
10.4.3 后台子服务程序实现
服务端子程序server_10.js代码如下:
function server_10(request, response, req_head, Q_obj, fs_obj) {
if (req_head == "/readXML_10") {
//代码1
fs_obj.readFile("./10/data/books.xml", "utf-8", function (err, data) {
if (err) { response.end(err.toString()); }
else { response.end(data); }
});
}
if (req_head == "/readXMLToTable_10") {
//代码2
fs_obj.readFile("./10/data/books.xml", "utf-8", function (err, data) {
if (err) { response.end(err.toString()); }
else {
var temp = data.replace("<books>", "<table border='1'><tr><th>书号</th><th>书名</th><th>价格</th></tr>");
temp = temp.replace("</books>", "</table>");
temp = temp.replace(/<book>/g, "<tr>");
temp = temp.replace(/<\ /book>/g, "</tr>");
temp = temp.replace(/(<ISBN>|<title>|<price>)/g, "<td>");
temp = temp.replace(/(<\ /ISBN>|<\ /title>|<\ /price>)/g, "</td>");
response.end(temp);
}
});
}
}
module.exports = server_10
10.4.4 实现效果
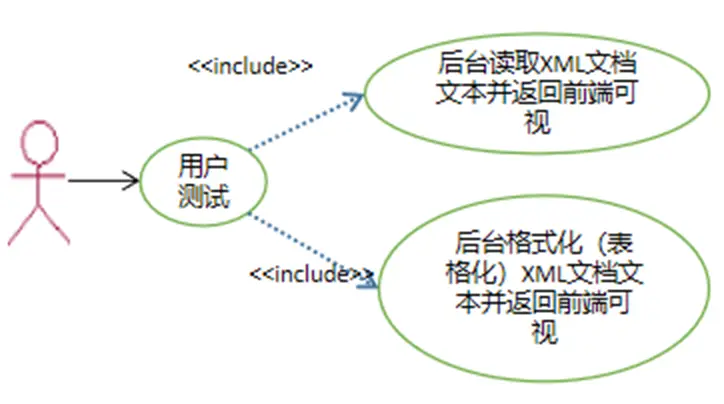
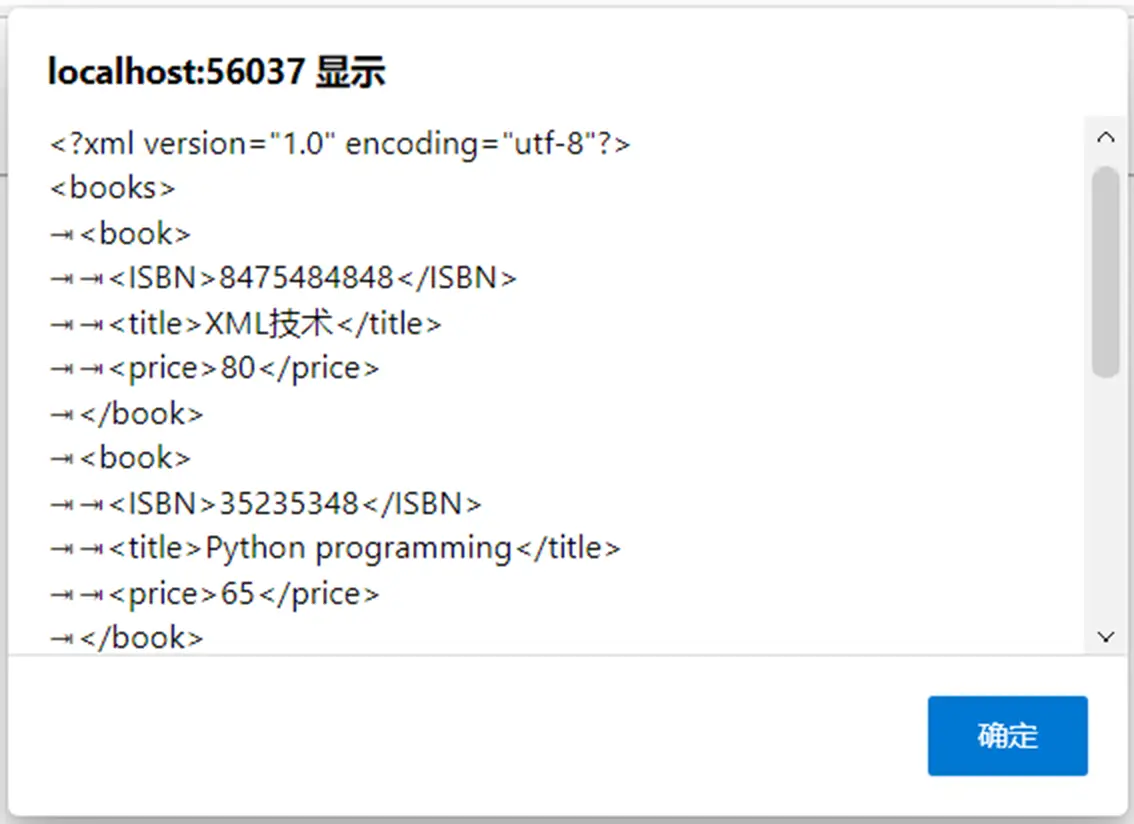
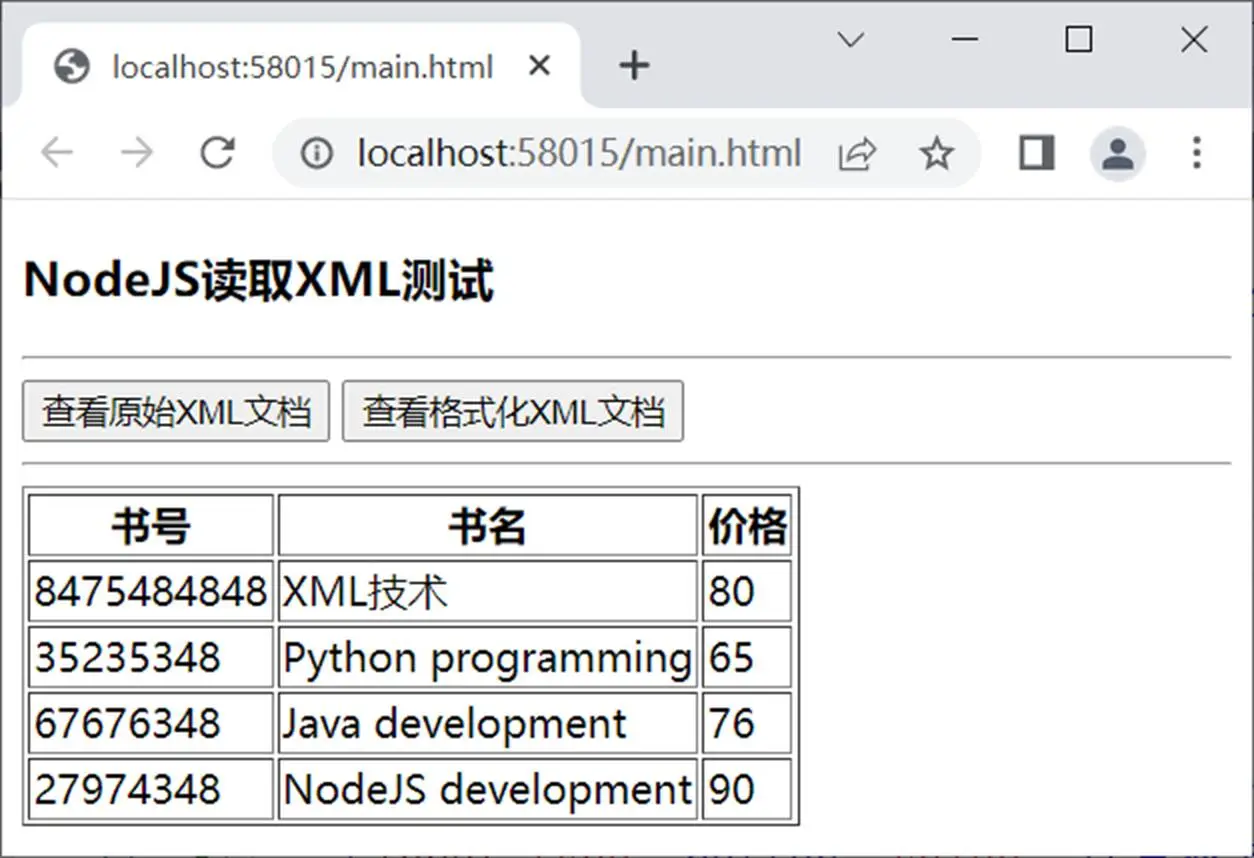
查看原始XML文档的实现效果如图10.5所示。
查看格式化XML文档(表格化)的实现效果如图10.6所示。
10.7 关于三层软件架构
三层软件架构因其低耦合性、可重用、标准化定义及良好的可伸缩性及可维护性而广泛应用于软件开发行业。在当今软件开发领域,面向对象分析方法是最典型、最常用的方法,面向对象分析方法认为系统是自包含的对象集合[1]。因此,在面向对象软件开发中,需要解决的核心问题是定义系统对象;然而,类是产生对象的通用模版。很显然,在面向对象软件开发中,需要解决的首要核心问题是定义系统中的类。在系统分析阶段,类可划分为实体类、控制类(用于描述一个或多个用例行为建模方式)、接口类[2]。用例是一系列行为活动的描述[3],因此,控制类是直接关系到软件功能实现的类,在软件分析和设计过程中,控制类的设计是一个非常重要的阶段。
三层架构是一种客户端-服务端架构,在三层架构中,用户界面、功能处理逻辑、计算机数据存储和存取是作为相对独立的模块进行开发和维护的[4]。在这一架构中,表示层、应用处理层和数据管理层在逻辑上是相对独立的并运行在不同的处理器上[5]。用户接口又叫作表示层[6];业务逻辑层是实现特定功能的核心层;数据访问层是从数据库获取数据并向业务逻辑层提供数据的类模块[7]。在三层架构中,客户端一般不直接访问数据库,但借助于位于中间层的COM/DCOM可建立与后台的连接;也就是说,客户端与数据库服务器的交互是通过叫业务逻辑层的中间层来实现的[8]。
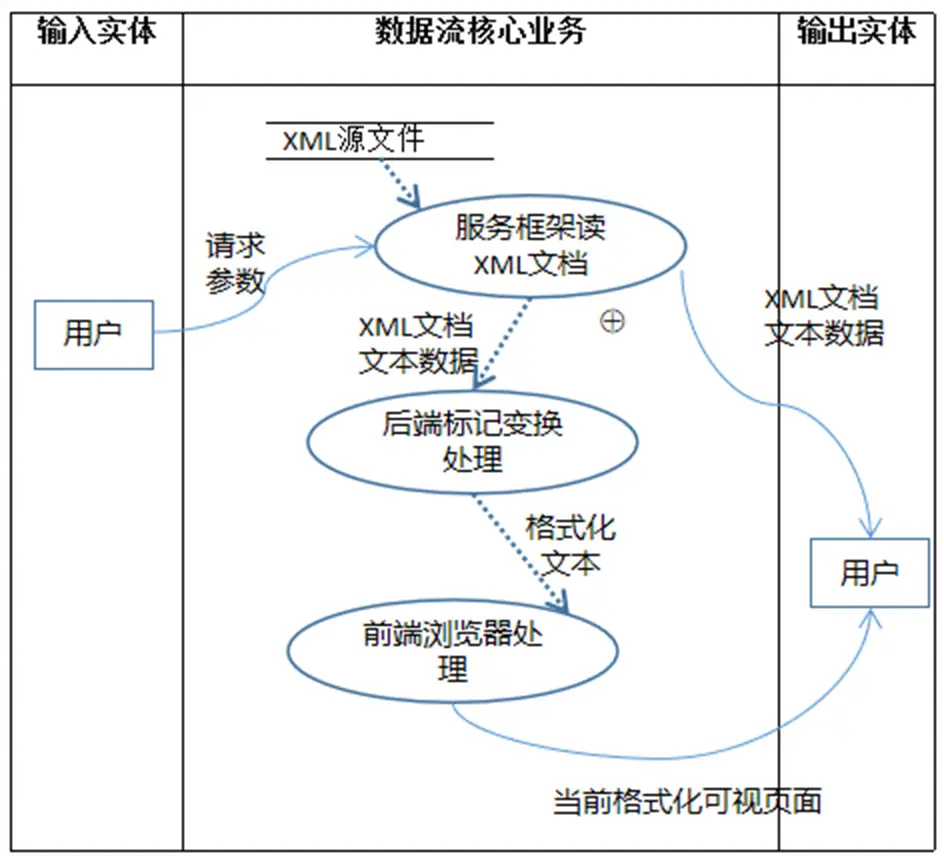
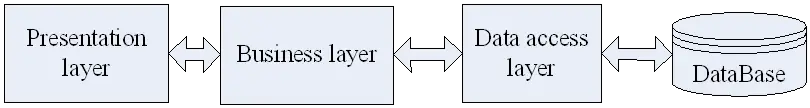
三层架构中数据存取之所以有良好的安全保障,很大程度上是由于实现了层的分离[9]。图10.7描述了三层架构的逻辑结构。
图10.4表明:表示层(Presentation layer)可直接与业务逻辑层(Business layer)通信;业务逻辑层可以直接与数据访问层(Data access layer)通信。事实上,层与层之间的通信是通过对象交互实现的。